In your daily tasks you create, save, edit things. You can be a designer, editor or a developer. Version Control systems give you the ability to keep track of what you did to the file, what you changed and what the contents of those changes are.
What is Version Control?
In your daily tasks you create, save, edit things. You can be a designer, editor or a developer. Version Control systems give you the ability to keep track of what you did to the file, what you changed and what the contents of those changes are.
For a single file and single individual this process could be relatively easy and managable. But for a team of designers or developers it gets extremely complicated. You need a central repository to keep track of all actions on the project files. That is where a Version Control Systems come in.
A Version Control System:
- Keep tracks of your creative output (e.g files, images)
- It tracks what is changed
- It tracks who makes the changes
- It tracks why the changes are made
There are multiple VCS on the market. Our topic is about Git and GitHub
What is Git:
“Git is a free and open source distributed version control system designed to handle everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency”
What is GitHub:
“GitHub is a web-based Git repository hosting service, which offers all of the distributed revision control and source code management (SCM) functionality of Git as well as adding its own features.”
Github provides access control and several collaboration features such as wikis, task management, and bug tracking and feature requests for every project.
You do not need GitHub to use Git. Please understand that > Git = Local (on you computer), GitHub = Remote (web).
Github allows you to:
- Access using a GUI
- Share your repositories with others.
- Access other user’s repositories. 4.Store remote copies of your repositories (github servers) as backup of your local copies.
How does git help you keep track of changes?
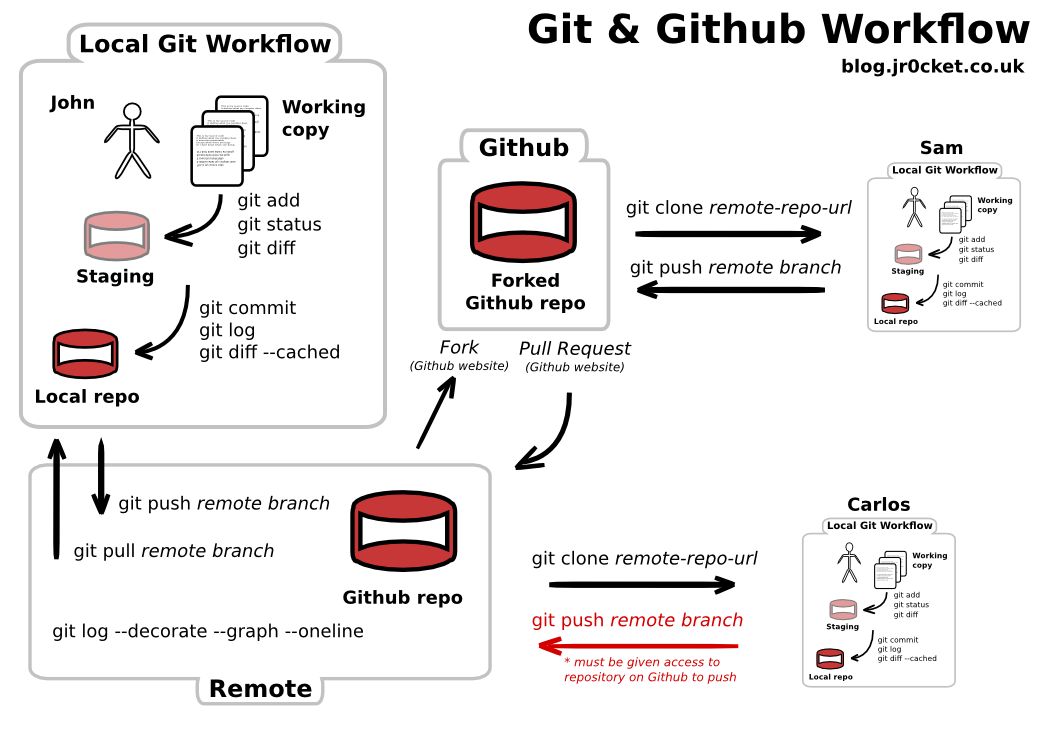
Tracking changes is done in a git branch. Master branch is automatically created. You may create others, then checkout to make it the active branch. Then hack away, edit files, delete them, add new ones, make symlinks and all that other fun stuff. A commit will then create a snapshot of your changes.
Once you are satisfied with your changes you can merge your branch with the Master.
Why use GitHub to store your code?

GitHub.com makes git accessible to everyone with a neat GUI. It also provides extensive features for colloboration. “Pull Request” is the most notable of all. Other features include:
File an issue about a project. Correct a defact. Track defacts. Comment on changes. Accept changes
Web flow also lets you rename, move and add files directly from the browser with the help of an online editor. This makes GitHub more accessible.
GitHub also has its own documentation format. .md extension files can be easily written using markdown language.
All these makes GitHub a good choice for VCS.
For a brief introduction to GitHub, please watch the video below…
Intro to GitHub • GitHub & Git Foundations from GitHub on Vimeo.
